Table of Contents
Introduction to OpenStack – A Comprehensive Beginner’s Guide
The advent of cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses and individuals deploy, manage, and scale applications and services. Amidst this transformative era, OpenStack emerges as a pivotal, open-source platform for cloud infrastructure, offering an array of IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) solutions. This guide embarks on an exploratory journey into the world of OpenStack, demystifying its architecture, core components, and delineating its unparalleled position in the cloud computing ecosystem.
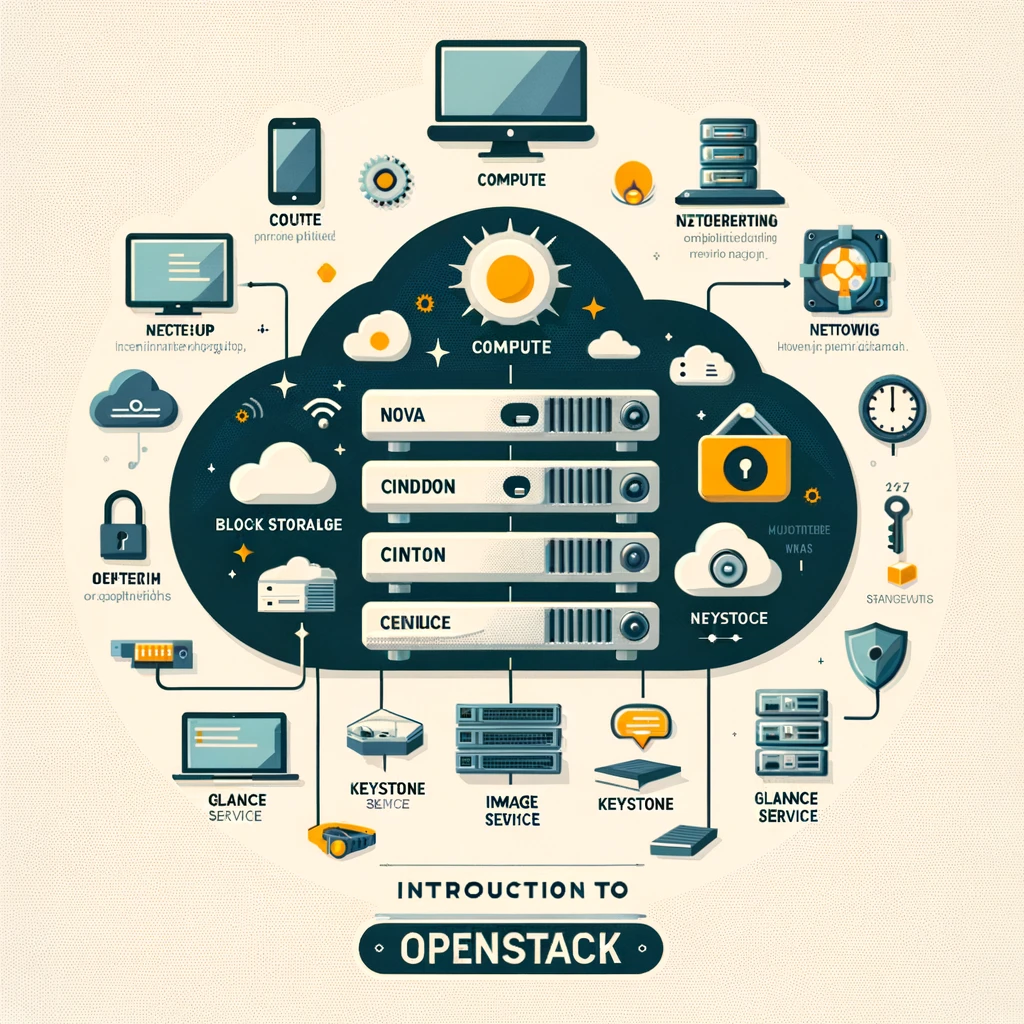
What is OpenStack?
OpenStack is a robust, open-source cloud computing platform that facilitates building and managing both public cloud and private cloud environments. It is developed by a vibrant community of contributors and is designed to be modular and flexible, capable of handling compute, storage, and networking resources across a data center. OpenStack enables businesses to deploy virtual machines and other instances which handle different tasks for managing a cloud environment on the fly.
The Core Architecture of OpenStack
OpenStack’s architecture is inherently modular, allowing users to implement various components independently or together, based on their specific needs. This modularity also facilitates scalability and integration, enabling the platform to serve as the foundation for a diverse range of cloud environments, from small private clouds to large public clouds.
The architecture of OpenStack is composed of several key components, each dedicated to a specific function within the cloud environment: Nova (Compute): Nova is the computing engine behind OpenStack, responsible for managing the lifecycle of compute instances in the OpenStack environment. It is capable of scaling horizontally on standard hardware, providing the power to grow or shrink compute resources as needed.
Swift (Object Storage): Swift offers object storage capabilities, allowing users to store and retrieve files. Unlike traditional file storage, object storage manages data as objects, making Swift ideal for unstructured data such as multimedia content, backups, and archives.
Cinder (Block Storage): Cinder provides persistent block storage to running instances. Its role is akin to that of traditional disk drives, allowing users to manage storage needs for their applications within the OpenStack environment dynamically.
Neutron (Networking): Neutron delivers “Networking as a Service” (NaaS) in OpenStack, managing the network connectivity and addressing within the cloud. It enables users to create their own networks and connect devices and instances as needed.
Keystone (Identity Service): Keystone plays a critical role in authentication and authorization for all OpenStack services. It maintains a directory of users mapped to the OpenStack services they can access, acting as a central identity service.
Glance (Image Service): Glance stores and retrieves disk and server images. These images are used as templates to deploy new instances, streamlining the process of launching virtual machines.
Horizon (Dashboard): Horizon is the graphical interface for OpenStack. It provides a web-based portal for users and administrators to interact with and manage the various components of the OpenStack cloud.
Why OpenStack Stands Out
OpenStack’s popularity in cloud computing stems from several key attributes:
Open-Source Nature: Being open-source, it fosters innovation, allowing developers to contribute and tailor the platform to meet their specific requirements.
Flexibility and Scalability: OpenStack’s modular architecture ensures that it can scale to meet the demands of small businesses and large enterprises alike.
Cost-Effectiveness: OpenStack can significantly reduce the cost of cloud computing by leveraging standard hardware and avoiding vendor lock-in.
Vibrant Community: A strong, global community of developers and users continuously enhances OpenStack’s capabilities and supports its adoption.
Conclusion
OpenStack represents a formidable framework in the domain of cloud computing, characterized by its flexibility, scalability, and community-driven development. As organizations continue to seek efficient, reliable, and scalable cloud solutions, OpenStack is poised to play a critical role in the evolution of cloud infrastructure. For beginners stepping into the cloud computing arena, understanding OpenStack’s foundational principles and architecture is a valuable asset, unlocking the potential to innovate and deploy versatile cloud environments tailored to diverse needs.
Blog Home
